About This Article:
A Delaware Statutory Trust (DST) is a powerful tool for investors looking to defer capital gains taxes through a 1031 exchange. By understanding the mechanics of a DST 1031 exchange, you can make informed decisions about your investment strategy.
What is a 1031 Exchange?
A 1031 exchange allows you to defer capital gains taxes when selling an investment property. To qualify, you must reinvest the proceeds from the sale into a similar property within a specific timeframe.
The Role of DSTs in 1031 Exchanges
DSTs offer a unique advantage in 1031 exchanges. They are professionally managed investment vehicles that pool funds from multiple investors to purchase a specific property or group of properties. This structure provides several benefits:
- Diversification: DSTs allow you to invest in a diversified portfolio of properties, reducing risk.
- Liquidity: DSTs often offer more liquidity than direct property ownership, making it easier to sell your investment if needed.
- Professional Management: DSTs are managed by experienced professionals who handle property management, tenant relations, and other administrative tasks.
- Accessibility: DSTs typically have lower minimum investment requirements than direct property ownership, making them more accessible to a wider range of investors.
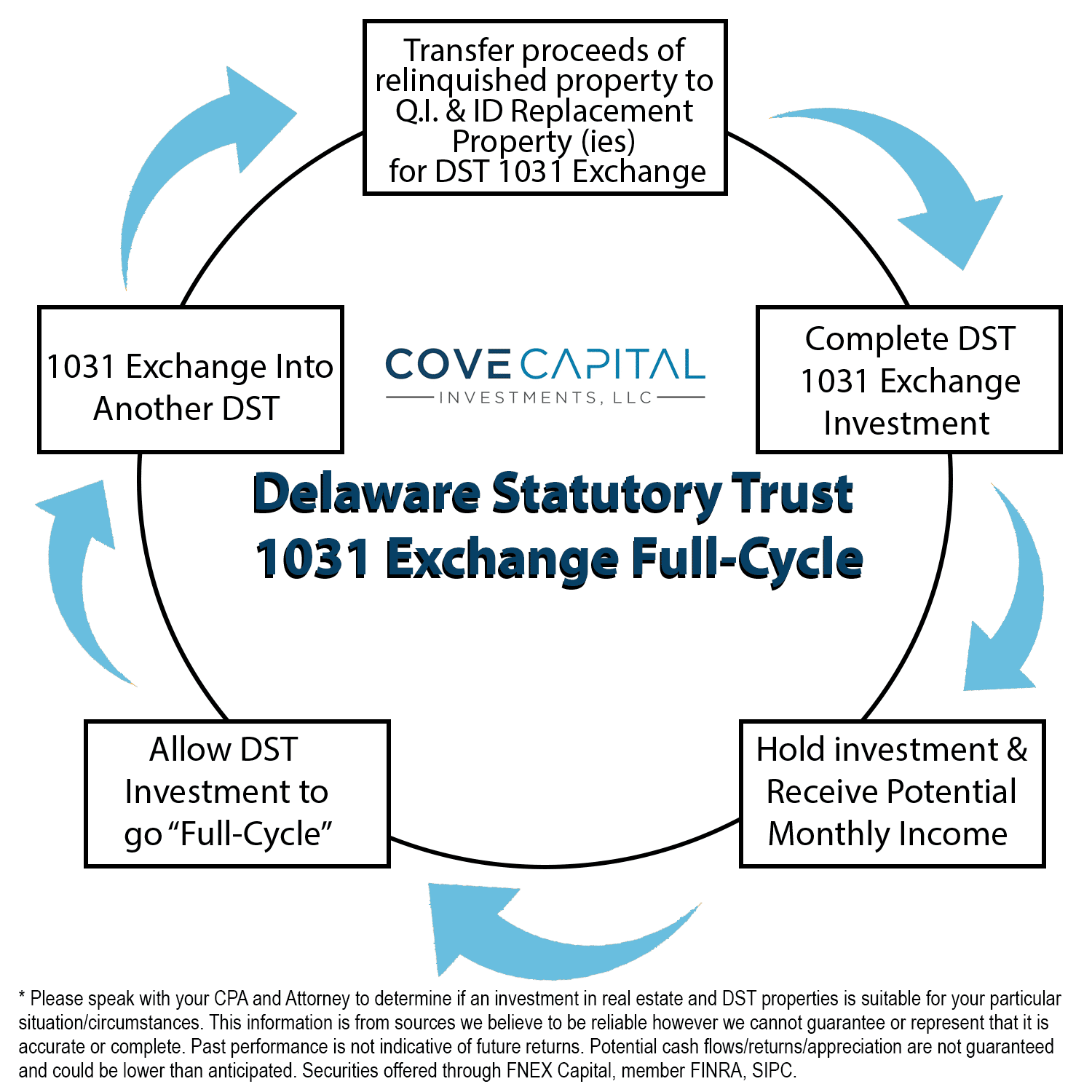
How Does a DST 1031 Exchange Work?
The process of a DST 1031 exchange involves several key steps:
- Identify a DST: Research DSTs that align with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
- Sell Your Property: Sell your existing property, ensuring that the proceeds are held in a qualified intermediary account.
- Purchase the DST: Use the proceeds from the sale to purchase shares in the DST.
- Meet IRS Requirements: Comply with all IRS regulations for 1031 exchanges, including deadlines and documentation.
Key Considerations for DST 1031 Exchanges
When considering a DST 1031 exchange, keep the following factors in mind:
- Fees and Expenses: DSTs typically involve fees, including management fees and acquisition fees.
- Liquidity: While DSTs offer more liquidity than direct property ownership, there may be restrictions on selling your shares.
- Risk: DSTs are not without risk. The value of your investment can fluctuate based on market conditions and the performance of the underlying properties.
- Tax Implications: While 1031 exchanges defer capital gains taxes, there may be other tax implications to consider, such as depreciation recapture.
DSTs can be a valuable tool for investors seeking to defer capital gains taxes through 1031 exchanges. By understanding the mechanics of DSTs and carefully considering the factors involved, you can make informed decisions about whether a DST is the right investment for you.